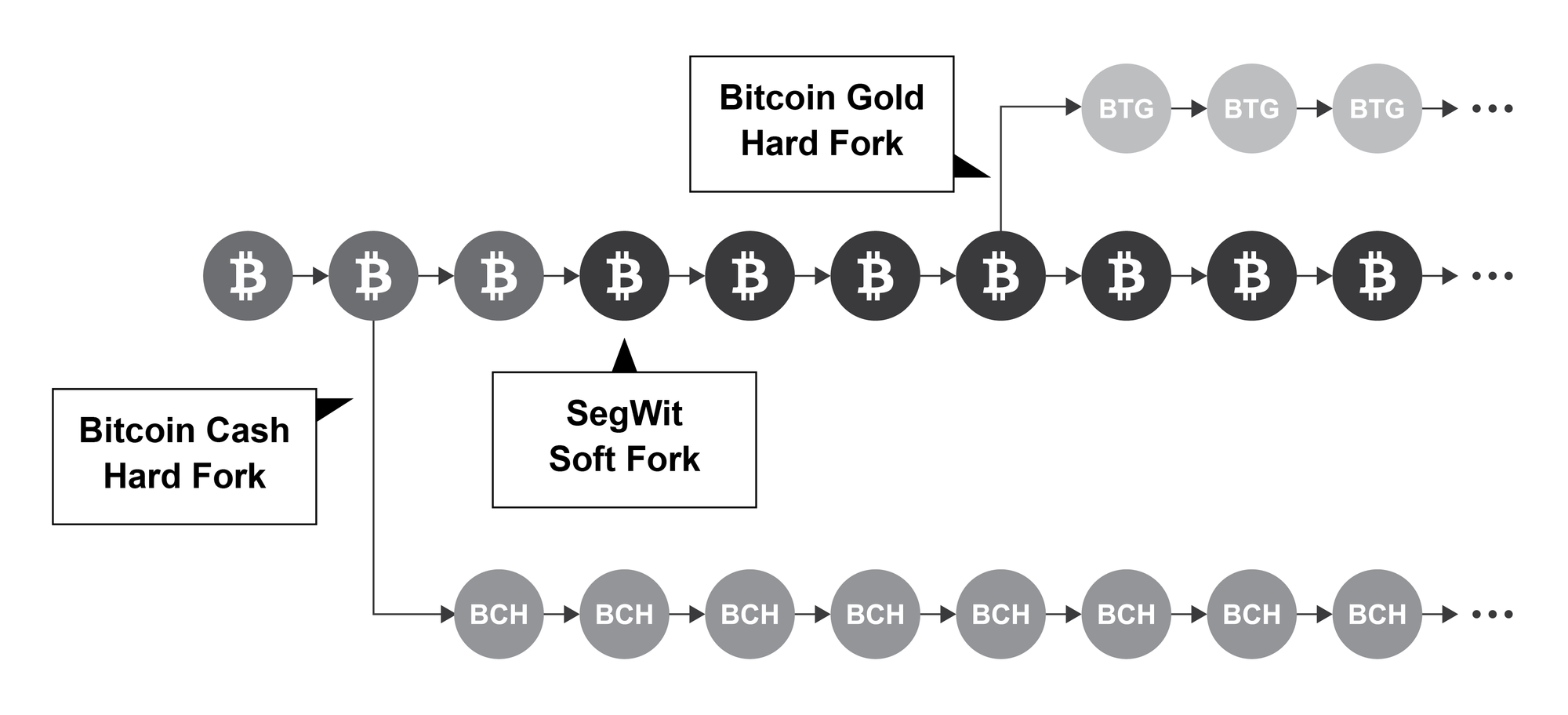
Fork
A fork in Bitcoin refers to a change in the protocol rules. There are two main types:
Hard fork: A change incompatible with previous versions, causing the blockchain to split into two if not all nodes upgrade. It results in an entirely new blockchain.
Soft fork: A backward-compatible change, meaning the new chain is still compatible with the old one. Older nodes see new transactions as valid (but may not understand them), ensuring a single continued chain. It tightens or adds rules without ostracizing previous nodes.
Two prominent soft forks in Bitcoin were Segregated Witness (SegWit) in 2017 and Taproot in 2021.